GridFTP: SC25 Test of Time Award
- Paper Reading
- 2025-10-10
- 328 Views
- 0 Comments
How to move massive data from server to client? How to serve multiple users around the world to use the compute machine?
This technology was not invented in cloud computing, but grid computing. And this is the paper published at SC05: The Globus Striped GridFTP Framework and Server.
SC25 ToT Award
From SC25 website:
https://sc25.supercomputing.org/2025/10/lasting-innovation-in-data-movement-sc25-test-of-time-award/
The SC25 Test of Time (ToT) committee is pleased to announce that The Globus Striped GridFTP Framework and Server by William Allcock, John Bresnahan, Rajkumar Kettimuthu, Michael Link, Catalin Dumitrescu, Ioan Raicu, and Ian Foster has been selected as the winner of this year’s award.
First published at SC05, this important paper addressed one of the central challenges in supercomputing at the time: how to move very large amounts of data both reliably and securely, without sacrificing performance. The authors’ solution, the striped GridFTP framework, made it possible for multiple servers and clients to work together in parallel, significantly increasing the scale and speed of transfers. At the time, these capabilities allowed data to move at rates far beyond what existing tools could support, while also serving thousands of users simultaneously.
The influence of this work has been profound. For nearly two decades, GridFTP provided the foundation for scientific discovery in many fields: enabling the movement of telescope sky survey data, supporting analysis from large particle accelerators, and helping transfer vast genomic datasets. It became a trusted and widely adopted tool for the global research community—well before today’s cloud-based approaches were available.
Reflecting on the award, SC25 Test of Time Award Chair Bill Gropp shared:
“The Globus Striped GridFTP paper represents a milestone in data movement for computational science. Its approach has been widely adopted and remains a critical part of the community’s infrastructure. Few technologies have had such a lasting impact, and this paper represents perfectly what our Test of Time Award is all about.”
Paper link:
https://www.globus.org/sites/default/files/gridftp_final.pdf
Introduction
The GridFTP extensions to the File Transfer Protocol define a general-purpose mechanism for secure, reliable, high-performance data movement.
The early 2000s saw a rapid increase in data volume and network capacity. However, moving large datasets across wide-area networks (WANs) was technically challenging due to:
- The need to exploit parallelism in storage, networks, and interfaces.
- Dealing with firewalls, heterogeneous systems, and frequent failures.
- TCP's inefficiency on high-bandwidth, high-latency links.
- The complexity of managing end-to-end performance across diverse devices
The authors chose to implement the GridFTP protocol, an extension of FTP, for its:
- Separation of control and data channels (enabling third-party transfers).
- Well-defined extension mechanism.
- Added features like striping, parallel streams, and partial file transfer.
Problem background
-
随着存储系统数据量和广域网带宽的快速增长,跨广域网高效、可靠地传输大规模数据变得日益重要。
-
传统FTP协议在性能、安全性和扩展性方面存在局限,无法满足高性能计算和大规模分布式系统的需求。
For example, the NSF TeraGrid network links large clusters and storage systems at nine sites with a network providing up to 30 Gbit/s end-to-end. In principle, we should be able to move data across this network at more than 3 Gbyte/s, or 10 Tbyte/hr.
In practice, the orchestration of such transfers is technically challenging. One key issue is the frequent need to exploit parallelism in multiple dimensions, including (depending on context) storage systems, network interfaces, and backbone network trunks. Another is dealing with failures of various sorts. Firewalls, parallel file systems, and other specialized devices can also cause difficulties, as can the need to transform data before and/or after transfer. For these and other reasons, rapid, efficient, and robust wide area end-to-end transport requires the management of complex systems at multiple levels. For example, in recent work, we required 32 hosts connected at 1 Gbit/s to drive a 30 Gbit/s connection.
Protocol Design
Key Features
- Striping & Parallelism: Data can be distributed across multiple servers (striping) and transferred using multiple parallel TCP streams to saturate high-speed links.
- OA/Security: Robust authentication using GSS-API (with GSI and Kerberos bindings) for both control and data channels, which is critical for third-party transfers.
- Third-Party Control: Allows a client to initiate and manage a transfer between two remote servers.
- Reliability: Supports restartable transfers from the point of failure.
GridFTP 是对标准FTP的扩展,增加了以下关键特性:
- 第三方控制传输
- GSS-API 认证(控制通道与数据通道)
- 并行TCP流+条纹化传输(多服务器并行传输)+ 部分文件传输
- 可靠与可恢复传输
The core innovation is the modular framework, which consists of three logical components:
- Protocol Interpreters (PIs): Handle the control channel communication (client and server).
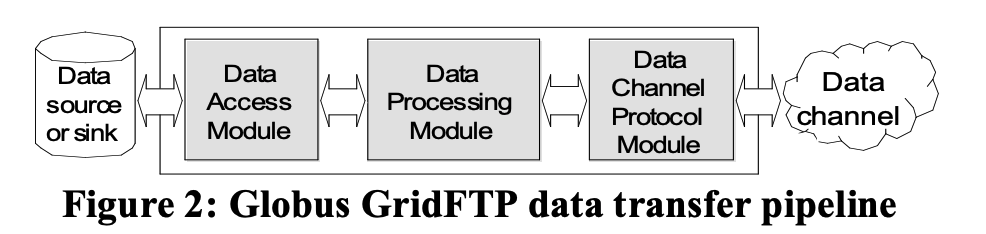
- Data Transfer Process (DTP): Handles the actual data movement. It is itself decomposed into a pipeline of three modules:
- Data Access Module: Interfaces with storage (e.g., POSIX files, HPSS).
- Data Processing Module: Performs server-side processing (e.g., compression).
- Data Channel Protocol Module: Manages the network protocol (using the Globus XIO system).
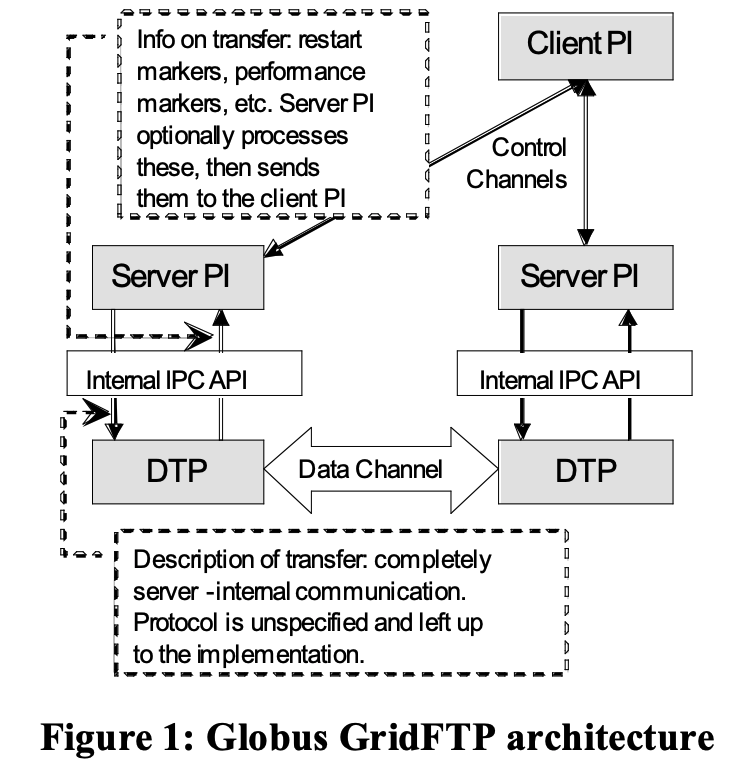
Globus GridFTP 系统采用模块化、可扩展的架构,主要包括三个组件:
- 协议解释器(PI):处理控制通道命令。
- 数据传输进程(DTP):负责实际的数据读写和传输。
- DTP 内部模块:
- 数据访问模块:读写本地或远程存储。
- 数据处理模块:支持服务器端数据转换(如压缩)。
- 数据通道协议模块:处理网络传输协议(如TCP)。
Experiment
speeds of 27.3 Gbit/s memory-to-memory and 17 Gbit/s disk-to-disk over a 60 millisecond round trip time, 30Gbit/s network
In another experiment, we show that the server can support 1800 concurrent clients without excessive load.
- 在WAN环境中,内存到内存传输可达 27.3 Gbit/s,磁盘到磁盘传输可达 17 Gbit/s。
- 系统支持 1800个并发客户端,表现出良好的可扩展性。
Globus Striped GridFTP 是一个高性能、模块化、可扩展的数据传输框架,适用于大规模、高并发的科学计算和数据密集型应用。其设计兼顾了性能、安全性和灵活性,为构建下一代数据管理工具提供了坚实基础。
